A) International treaties
B) The growth of trade
C) Commodity indexes
D) The growth of the stock of gold
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An example of a fixed exchange rate was the gold standard.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Perfect mobility of factors of production is a requirement for
A) Spatially concentrated trade zones
B) Optimal currency areas
C) Commodity money standards
D) Free floating exchange rates
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What exchange rate is maintained with a central rate that is frequently adjusted?
A) Fixed Peg
B) Currency board
C) Managed floating
D) Crawling bands
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The geographic area that would maximize economic benefits by keeping the exchange rate fixed within the area is a an) :
A) Trade union
B) Currency board
C) Trade bloc
D) Optimal currency area
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A managed floating exchange rate is a market determined exchange system as long as rates stay between target zones as mandated by legislative commitments.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gold standard was an example of:
A) An optimum currency area
B) A commodity money standard
C) A standard currency board
D) All of the above
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Countries use reserve currencies as an international unit of account, a medium of exchange, and a store of value.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following economies has adopted a "currency board" exchange rate system?
A) Malaysia
B) South Korea
C) China
D) Hong Kong
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the graph below to answer questions
Figure 2.3:
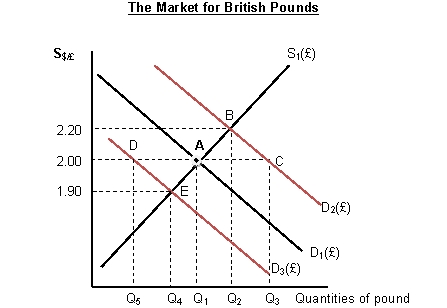 -Refer to Figure 2.3. Suppose that the spot exchange rate of British pound is $2.00 per pound. Suppose that the U.S. decreases its imports from the U.K. Under flexible exchange rate system, the Bank of England will:
-Refer to Figure 2.3. Suppose that the spot exchange rate of British pound is $2.00 per pound. Suppose that the U.S. decreases its imports from the U.K. Under flexible exchange rate system, the Bank of England will:
A) let the British pound appreciates
B) let the British pound depreciates
C) sell pounds and buy dollars in foreign exchange market.
D) sell dollars and buy pounds in foreign exchange market.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Destabilizing speculation is the process where
A) In a free floating exchange system, speculators cause wide fluctuations to the exchange rate.
B) In a fixed peg exchange system, speculators hold foreign reserves too long and destabilize the peg.
C) In a free floating exchange system, the International Monetary Fund is forced to issue Special Drawing Rights.
D) In a fixed peg exchange system, speculators sell all holdings of Special Drawing Rights.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In general, the smaller the country is, the more likely it is to peg its exchange rate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
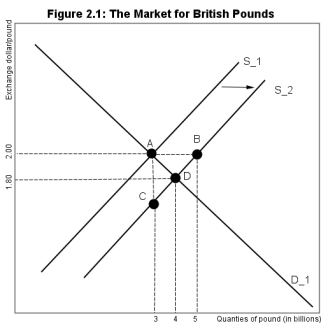 -Referring to Figure 2.1, the pound per dollar exchange rate starts at 2.00. Assume that an increase in the taste for U.S. imports by U.K. residents leads to a shift in the supply of pounds. If the Bank of England wishes to intervene by buying pounds to restore the peg of $2.0/pound, what distance represents that intervention?
-Referring to Figure 2.1, the pound per dollar exchange rate starts at 2.00. Assume that an increase in the taste for U.S. imports by U.K. residents leads to a shift in the supply of pounds. If the Bank of England wishes to intervene by buying pounds to restore the peg of $2.0/pound, what distance represents that intervention?
A) A to B
B) B to A
C) A to D
D) D to B
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A pegged exchange rate is: I. Fixed to a currency or basket of currencies II) Responds to indicators such as inflation differentials) III) May require intervention to maintain the target pegged rate
A) I only
B) III only
C) I and III
D) I, II, and III
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the market for Chinese currency yuan) . Suppose that the initial equilibrium exchange rate was $0.125 per one yuan. Then assume that American consumers like Chinese products more than before. If China's central bank wants to peg the exchange rate at its initial level $0.125 per yuan) , the central bank will have to
A) buy yuan and sell dollar.
B) sell yuan and buy dollar.
C) buy yuan and buy dollar.
D) sell yuan and sell dollar.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of an optimal currency area would be
A) United States
B) Southeast Asia
C) Latin America
D) Both A and C
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The International Monetary Fund was created at the beginning of the:
A) Bretton Woods system
B) Gold standard
C) Interwar period
D) Smithsonian agreement
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following exchange rate systems is the least flexible?
A) Free floating
B) Managed floating.
C) Currency board
D) Fixed peg arrangement
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the United States suspended the convertibility of dollars into gold in 1971, this lead to:
A) The collapse of the Bretton Woods system
B) Creation of the regional currency boards
C) Creation of the International Monetary Fund
D) All of the above
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bretton Woods agreement required that each country, other than the U.S., fix the value of its currency in terms of an) :
A) Ounce of gold
B) Common currency
C) Commodity basket
D) Anchor currency
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 52
Related Exams