A) an attainable combination of Good A and Good B.
B) an unattainable combination of Good A and Good B.
C) the combination of Good A and Good B that the economy will produce.
D) one possible efficient combination of Good A and Good B.
E) the only unattainable combination of Good A and Good B.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The law of comparative advantage states that the person who should produce a good is the person who:
A) has the lowest opportunity cost of producing that good.
B) can produce that good using the fewest resources.
C) will produce that good using the most expensive resources.
D) has the most desire for that good.
E) has produced that good in the past.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An improvement in technology:
A) will always result in a parallel shift of the production possibilities frontier.
B) will never result in a parallel shift of the production possibilities frontier.
C) will be indicated as a movement along the production possibilities frontier.
D) will shift the production possibilities frontier outward but not necessarily to a parallel position.
E) may not shift the production possibilities frontier.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A production possibilities frontier can shift outward for all of the following reasons except:
A) a decrease in the size of the labor force.
B) an increase in the skills of the labor force.
C) an improvement in technology.
D) a larger work force.
E) a larger capital stock.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In one week, Mohammed can knit 5 sweaters or bake 240 cookies. In one week, Aisha can knit 15 sweaters or bake 480 cookies. Aisha's opportunity cost of knitting one sweater is:
A) 240 cookies.
B) 480 cookies.
C) 32 cookies.
D) 1/32 of a cookie.
E) 16 cookies.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At all points along the production possibilities frontier, _____.
A) the greatest achievable output levels are illustrated
B) resources are not fully employed
C) more of one good can be obtained without giving up more of the other
D) more efficient output levels are possible
E) society is equally well off
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a command economy, _____.
A) a dictator makes every economic decision
B) owners can sell their resources to the highest bidder
C) no individual or group coordinates the economy
D) in theory, individual choices are reflected in collective decisions and decisions are made by central planners.
E) public ownership of resources is combined with free markets to direct economic activity
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The production possibilities frontier represents all desirable combinations of outputs.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would shift the production possibilities frontier outward?
A) An increase in the size of the labor force
B) More efficient use of existing resources and technology
C) The government prints more money
D) The end of a strike by a labor union
E) Society's desire to produce more of one of the goods
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A test is scheduled for Monday morning, and you went to a party on Sunday night. If you hadn't attended the party, you could have studied for the test or gone to a movie. Which of the following is true regarding your opportunity cost?
A) The opportunity cost of going to the movie is studying for the test.
B) The opportunity cost of going to the party is watching the movie.
C) The opportunity cost of going to the party is both watching the movie and the study time.
D) Because you could go to the party only that night, but could go to a movie any time, the opportunity cost of the party is the study time.
E) From the above information, it's not possible to determine the opportunity cost of attending the party.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the production possibilities frontier for education and food production. Which of the following would cause the production possibilities frontier to shift from AA to BA?
Figure 2.6
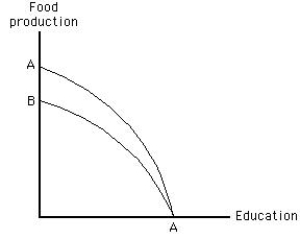
A) A drought that affected food production but had no effect on education.
B) A technological improvement in education that had no effect on food production.
C) A technological improvement in food production that had no effect on education.
D) A disease that affected students' ability to learn (and therefore education) but not food production.
E) An increase in the size of the labor force that affected both food production and education.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below shows the production possibilities frontier for mufflers and socks. The opportunity cost of moving from point b to d is:
Figure 2.4
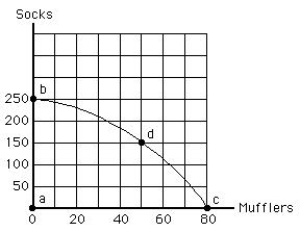
A) 30 mufflers.
B) 50 mufflers.
C) 100 socks.
D) 150 socks.
E) 250 socks.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you have an hour before your next class starts. You can either read a book, get something to eat, or take a nap. The opportunity cost of getting something to eat is:
A) the cost of what you eat.
B) the value of reading and sleeping.
C) the loss of value from not reading or sleeping.
D) the net benefit of sleeping for another hour.
E) impossible to determine because the most preferred alternative is not known.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Points inside the production possibilities frontier represent:
A) full and efficient use of all resources.
B) inefficiency or unemployment.
C) currently unattainable combinations of outputs.
D) currently unattainable combinations of resources.
E) the most desirable combinations of outputs.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A downward-sloping straight-line production possibilities frontier indicates:
A) that society cannot decide which good it prefers.
B) an absence of scarcity.
C) constant opportunity cost.
D) inefficiency.
E) specialization.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below shows the production possibilities frontier for mufflers and socks. If society moves from point c to point d, then society:
Figure 2.4
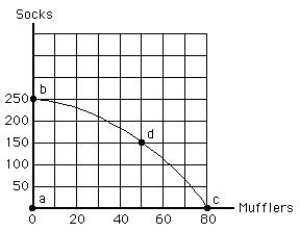
A) gains 100 socks.
B) loses 30 mufflers.
C) is worse off after the change in production.
D) is not operating efficiently.
E) experiences some unemployment of resources.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Each point on a production possibilities frontier requires full employment of resources.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The opportunity cost of going to college consists of more than just the tuition that will be paid.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On a bowed-out production possibilities frontier showing possible output levels of Good A and good B, the opportunity cost of producing the first 10 units of Good A will usually be:
A) the same as the opportunity cost of producing the next 10 units of Good A.
B) lower than the opportunity cost of producing the next 10 units of Good A.
C) greater than the opportunity cost of making the next 10 units of Good A.
D) 10 units of Good A.
E) 10 units of Good B.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On a given production possibilities frontier, which of the following is not assumed to be fixed?
A) The amount of labor available
B) The amount of capital available
C) The level of technology
D) The amount of land and natural resources available
E) Production of each item
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 159
Related Exams