A) $0.95
B) $1.05
C) $1.16
D) $1.27
E) $1.40
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Jameson Company just paid a dividend of $0.75 per share,and that dividend is expected to grow at a constant rate of 5.50% per year in the future.The company's beta is 1.15,the market risk premium is 5.00%,and the risk-free rate is 4.00%.What is Jameson's current stock price,P0?
A) $18.62
B) $19.08
C) $19.56
D) $20.05
E) $20.55
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Young & Liu Inc.'s free cash flow during the just-ended year (t = 0) was $100 million,and FCF is expected to grow at a constant rate of 5% in the future.If the weighted average cost of capital is 15%,what is the firm's value of operations,in millions?
A) $948
B) $998
C) $1,050
D) $1,103
E) $1,158
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The projected cash flow for the next year for Minesuah Inc.is $100,000,and FCF is expected to grow at a constant rate of 6%.If the company's weighted average cost of capital is 11%,what is the value of its operations?
A) $1,714,750
B) $1,805,000
C) $1,900,000
D) $2,000,000
E) $2,100,000
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A company is expected to have free cash flows of $0.75 million next year.The weighted average cost of capital is WACC = 10.5%,and the expected constant growth rate is g = 6.4%.The company has $2 million in short-term investments,$2 million in debt,and 1 million shares.What is the stock's current intrinsic stock price?
A) $17.39
B) $17.84
C) $18.29
D) $18.75
E) $19.22
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a company's free cash flows are expected to grow at a constant rate of 5% a year,which of the following statements is CORRECT? The stock is in equilibrium.
A) The company's stock's dividend yield is 5%.
B) The value of operations is expected to decline in the future.
C) The company's WACC must be equal to or less than 5%.
D) The company's value of operations one year from now is expected to be 5% above the current price.
E) The expected return on the company's stock is 5% a year.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is NOT CORRECT?
A) The free cash flow valuation model discounts free cash flows by the required return on equity.
B) The free cash flow valuation model can be used to find the value of a division.
C) An important step in applying the free cash flow valuation model is forecasting the firm's pro forma financial statements.
D) Free cash flows are assumed to grow at a constant rate beyond a specified date in order to find the horizon, or terminal, value.
E) The free cash flow valuation model can be used both for companies that pay dividends and those that do not pay dividends.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Connor Publishing's preferred stock pays a dividend of $1.00 per quarter,and it sells for $55.00 per share.What is its effective annual (not nominal) rate of return?
A) 6.62%
B) 6.82%
C) 7.03%
D) 7.25%
E) 7.47%
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If a stock has a required rate of return rs = 12% and its dividend is expected to grow at a constant rate of 5%, this implies that the stock's dividend yield is also 5%.
B) The stock valuation model, P0 = D1/(rs − g) , can be used to value firms whose dividends are expected to decline at a constant rate, i.e., to grow at a negative rate.
C) The price of a stock is the present value of all expected future dividends, discounted at the dividend growth rate.
D) The constant growth model cannot be used for a zero growth stock, where the dividend is expected to remain constant over time.
E) The constant growth model is often appropriate for evaluating start-up companies that do not have a stable history of growth but are expected to reach stable growth within the next few years.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Founders' shares are a type of classified stock where the shares are owned by the firm's founders,and they generally have more votes per share than the other classes of common stock.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carby Hardware has an outstanding issue of perpetual preferred stock with an annual dividend of $7.50 per share.If the required return on this preferred stock is 6.5%,at what price should the preferred stock sell?
A) $104.27
B) $106.95
C) $109.69
D) $112.50
E) $115.38
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stocks A and B have the following data.Assuming the stock market is efficient and the stocks are in equilibrium,which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Stock A has a higher dividend yield than Stock B.
B) Currently the two stocks have the same price, but over time Stock B's price will pass that of A.
C) Since Stock A's growth rate is twice that of Stock B, Stock A's future dividends will always be twice as high as Stock B's.
D) The two stocks should not sell at the same price. If their prices are equal, then a disequilibrium must exist.
E) Stock A's expected dividend at t = 1 is only half that of Stock B.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A stock just paid a dividend of D0 = $1.50.The required rate of return is rs = 10.1%,and the constant growth rate is g = 4.0%.What is the current stock price?
A) $23.11
B) $23.70
C) $24.31
D) $24.93
E) $25.57
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The free cash flows (in millions) shown below are forecast by Simmons Inc.If the weighted average cost of capital is 13% and the free cash flows are expected to continue growing at the same rate after Year 3 as from Year 2 to Year 3,what is the Year 0 value of operations,in millions? 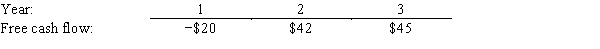
A) $586
B) $617
C) $648
D) $680
E) $714
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) The preemptive right gives stockholders the right to approve or disapprove of a merger between their company and some other company.
B) The preemptive right is a provision in the corporate charter that gives common stockholders the right to purchase (on a pro rata basis) new issues of the firm's common stock.
C) The stock valuation model, P0 = D1/(rs − g) , cannot be used for firms that have negative growth rates.
D) The stock valuation model, P0 = D1/(rs − g) , can be used only for firms whose growth rates exceed their required returns.
E) If a company has two classes of common stock, Class A and Class B, the stocks may pay different dividends, but under all state charters the two classes must have the same voting rights.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The free cash flow valuation model cannot be used unless a company doesn't pay dividends.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Two firms with the same expected dividend and growth rates must also have the same stock price.
B) It is appropriate to use the constant growth model to estimate a stock's value even if its growth rate is never expected to become constant.
C) If a stock has a required rate of return rs = 12%, and if its dividend is expected to grow at a constant rate of 5%, this implies that the stock's dividend yield is also 5%.
D) The price of a stock is the present value of all expected future dividends, discounted at the dividend growth rate.
E) The constant growth model takes into consideration the capital gains investors expect to earn on a stock.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The last dividend paid by Wilden Corporation was $1.55.The dividend growth rate is expected to be constant at 1.5% for 2 years,after which dividends are expected to grow at a rate of 8.0% forever.The firm's required return (rs) is 12.0%.What is the best estimate of the current stock price?
A) $37.05
B) $38.16
C) $39.30
D) $40.48
E) $41.70
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm's expected growth rate increased then its required rate of return would
A) decrease.
B) fluctuate less than before.
C) fluctuate more than before.
D) possibly increase, possibly decrease, or possibly remain constant.
E) increase.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You,in analyzing a stock,find that its expected return exceeds its required return.This suggests that you think
A) the stock should be sold.
B) the stock is a good buy.
C) management is probably not trying to maximize the price per share.
D) dividends are not likely to be declared.
E) the stock is experiencing supernormal growth.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 91
Related Exams