A) a necessity.
B) an abnormal good.
C) a normal good.
D) an inferior good.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
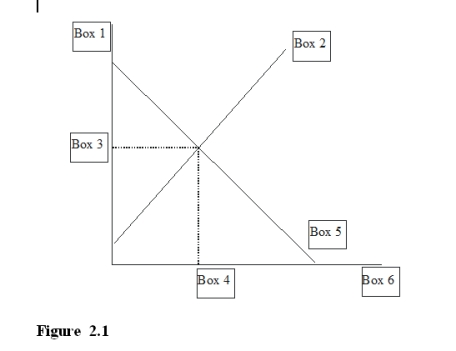 -In Figure 2.1, Box 5 would be labeled
-In Figure 2.1, Box 5 would be labeled
A) P* for equilibrium price.
B) P for price.
C) S for supply.
D) D for demand.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a tax (paid by consumers) is levied on a good this would
A) move its demand curve to the right.
B) move its demand curve to the left.
C) cause a movement along the demand curve to a (higher price, lower quantity) point.
D) cause a movement along the demand curve to a (lower price, higher quantity) point.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The increase in technology used to produce a good would
A) move its supply curve to the right.
B) move its supply curve to the left.
C) cause a movement along the supply curve to a (higher price, higher quantity) point.
D) cause a movement along the supply curve to a (lower price, lower quantity) point.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amount of money that must be paid per unit of output is called the
A) market.
B) equilibrium.
C) wage.
D) price.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The decrease in the price of a good that is another potential output for another good, would (for the second good)
A) move its supply curve to the right.
B) move its supply curve to the left.
C) cause a movement along the supply curve to a (higher price, higher quantity) point.
D) cause a movement along the supply curve to a (lower price, lower quantity) point.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the number of sellers increases, the
A) demand curve will shift to the right.
B) supply curve will shift to the right.
C) demand curve will shift to the left.
D) supply curve will shift to the left.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amount consumers are willing and able to buy at a particular price during a specified period of time is the
A) demand.
B) supply.
C) quantity demanded.
D) quantity supplied.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The substitution effect suggests that
A) when prices are higher your buying power is less so you buy less.
B) when prices are higher you buy less of what you originally wanted and use something else instead.
C) when prices are higher buy fewer because the marginal utility of a good is diminishing.
D) when prices are higher you buy more.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If demand increases and the price doesn't change, there will be a
A) surplus.
B) both a shortage and a surplus.
C) shortage.
D) neither a shortage nor a surplus.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there is an expectation that the price of a good will increase in the next month this would immediately
A) move its demand curve to the right.
B) move its demand curve to the left.
C) cause a movement along the demand curve to a (higher price, lower quantity) point.
D) cause a movement along the demand curve to a (lower price, higher quantity) point.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If two goods are considered substitutes and the price of one decreases, the other good's
A) demand curve will shift to the right.
B) supply curve will shift to the right.
C) demand curve will shift to the left.
D) supply curve will shift to the left.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mechanism by which buyers and sellers negotiate an exchange is called a/an
A) equilibrium.
B) model.
C) market.
D) meeting.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in household income for a good that is considered inferior would
A) move its demand curve to the right.
B) move its demand curve to the left.
C) cause a movement along the demand curve to a (higher price, lower quantity) point.
D) cause a movement along the demand curve to a (lower price, higher quantity) point.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If technology increases then
A) the demand curve will shift to the right.
B) the demand curve will shift to the left.
C) the supply curve will shift to the right.
D) the supply curve will shift to the left.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If two goods are considered complements and the price of one decreases then the other good's
A) demand curve will shift to the right.
B) supply curve will shift to the right.
C) demand curve will shift to the left.
D) supply curve will shift to the left.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
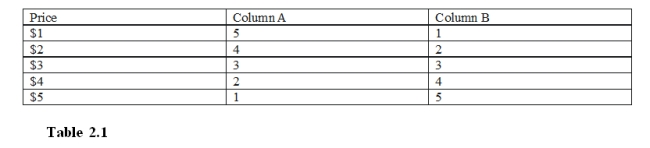 -From Table 2.1, which column is likely to be the one for quantity supplied?
-From Table 2.1, which column is likely to be the one for quantity supplied?
A) column A
B) neither A nor B
C) column B
D) either A or B are equally likely
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you are grocery shopping and you see that the price of beef has risen and as a result you change your planned menu for the week and buy chicken instead, the reason your demand curve for beef is downward sloping has mostly to do with
A) the substitution effect.
B) the real-balances effect.
C) diminishing marginal utility.
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the subsidy paid to producers of tobacco
A) shifts the supply of tobacco to the right.
B) shifts the demand for tobacco to the left.
C) shifts the demand for tobacco to the right.
D) shifts the market price of tobacco.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
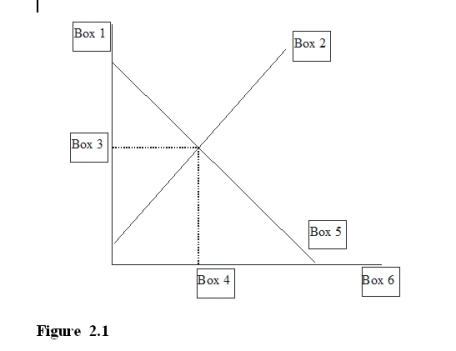 -In Figure 2.1, a "q/t" for quantity per unit time price would go in
-In Figure 2.1, a "q/t" for quantity per unit time price would go in
A) Box 1.
B) Box 2.
C) Box 4.
D) Box 6.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 204
Related Exams