A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The two "goods" used when economists analyze labor supply are
A) work and leisure.
B) work and consumption.
C) saving and consumption.
D) leisure and consumption.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-7 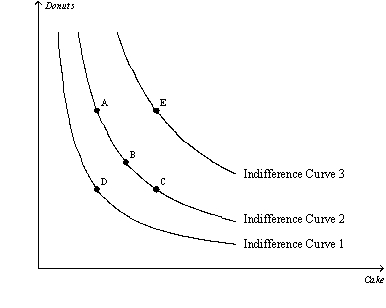 -Refer to Figure 21-7.Which of the following statements is correct?
-Refer to Figure 21-7.Which of the following statements is correct?
A) If a consumer moves from bundle C to bundle A,her loss of cake cannot be compensated for by an increase in donuts.
B) Bundle E is preferred to all other points identified in the figure.
C) Since more is preferred to less,bundle C may be preferred to bundle E in some circumstances for this consumer.
D) Even though bundle E has more of both goods than bundle B,we could draw a different set of indifference curves in which bundle B is preferred to bundle E.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carlos goes to the movies every Sunday afternoon.The movie theater offers 4 combinations of popcorn and beverages: the "mini-combo" costs $5 and includes a small popcorn and a small drink,the "medium-combo" costs $7 and includes a medium popcorn and a medium drink,the "value-combo" also costs $7 and includes a small popcorn and a large drink,and the "large-combo" costs $9 and includes a large popcorn and a large drink.Carlos always purchases the "value-combo." We can conclude that
A) Carlos cannot afford the "large-combo."
B) Carlos cannot afford the "medium-combo."
C) Carlos prefers a combo with a larger popcorn-to-beverage ratio.
D) Carlos prefers a combo with a smaller popcorn-to-beverage ratio.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer
A) is equally satisfied with any indifference curve.
B) prefers indifference curves with positive slopes.
C) prefers higher indifference curves to lower indifference curves.
D) prefers indifference curves that are straight lines to indifference curves that are right angles..
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the price of good X falls.As a result,the quantity demanded for good X increases for a particular consumer.For this consumer,the substitution effect induced the consumer to purchase more X while the income effect induced the consumer to purchase less X.We can infer that X is a(n)
A) normal good.
B) inferior good.
C) Giffen good.
D) luxury good.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An optimizing consumer will select a consumption bundle in which
A) income is maximized,and prices are minimized.
B) utility is maximized,and prices are minimized.
C) utility is maximized,subject to budget constraints.
D) utility is maximized,and indifference curves are linear.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 21-1 Suppose the price of hot wings is $10,the price of beer is $1,and the consumer's income is $50.In addition,suppose the consumer's budget constraint illustrates hot wings on the horizontal axis and beer on the vertical axis. -Refer to Scenario 21-1.If the price of beer doubles to $2,then the
A) budget constraint intersects the vertical axis at 25 beers.
B) slope of the budget constraint rises to -2.
C) budget constraint intersects the vertical axis at 100 beers.
D) budget constraint shifts inward in a parallel fashion.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer's preferences for right shoes and left shoes can be represented by indifference curves that are
A) bowed out from the origin
B) bowed in toward the origin
C) straight lines
D) right angles
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An inferior good is one in which
A) the average consumer chooses not to consume.
B) the good is not equally valued by all consumers.
C) an increase in income increases consumption of the good.
D) an increase in income decreases consumption of the good.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The opportunity cost of current household consumption is the
A) wage rate.
B) market interest rate.
C) price of the goods consumed.
D) explicit cost of consumption.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If Walter has one hour of leisure time in which to watch a sporting event on television,his preferences are as follows: Walter prefers watching football to watching baseball,but he prefers watching baseball to watching basketball.He is indifferent between watching baseball and watching hockey.Bundle A contains one hour of football and zero hours of all other sports.Bundle B contains one hour of baseball and zero hours of all other sports.Bundle C contains one hour of basketball and zero hours of all other sports.Bundle D contains one hour of hockey and zero hours of all other sports.If we were to graph Walter's preferences using indifference curves,which of the following bundles would be on the same indifference curve?
A) A,B,and C only
B) B and D only
C) A and D only
D) There is no combination of the sports that could be drawn on the same indifference curve.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rational consumer maximizes her
A) preferences.
B) marginal rate of substitution.
C) utility.
D) budget constraint.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-4 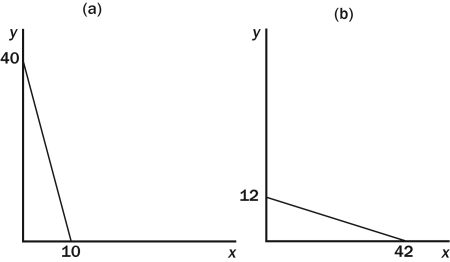 -Refer to Figure 21-4.In graph (a) ,if income is equal to $120,the price of good Y is
-Refer to Figure 21-4.In graph (a) ,if income is equal to $120,the price of good Y is
A) $1
B) $2
C) $3
D) $4
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 341 - 354 of 354
Related Exams