A) there are no H⁺ ions in the water.
B) this is a solution of pure water.
C) the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water equals the concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water.
D) this is a solution of pure water, and the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water is 10⁻⁷ M.
E) this is a solution of pure water, and the concentration of H⁺ ions equals the concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identical heat lamps are arranged to shine on identical containers of water and methanol (wood alcohol) , so that each liquid absorbs the same amount of energy minute by minute. The covalent bonds of methanol molecules are nonpolar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules. Which of the following graphs correctly describes what will happen to the temperature of the water and the methanol?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Temperature usually increases when water condenses. Which behavior of water is most directly responsible for this phenomenon?
A) the change in density when it condenses to form a liquid or solid
B) reactions with other atmospheric compounds
C) the release of heat by the formation of hydrogen bonds
D) the release of heat by the breaking of hydrogen bonds
E) the high surface tension of water
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a hydrophobic material?
A) paper
B) table salt
C) wax
D) sugar
E) pasta
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true about buffer solutions?
A) They maintain a constant pH when bases are added to them but not when acids are added to them.
B) They maintain a constant pH when acids are added to them but not when bases are added to them.
C) They maintain a relatively constant pH of approximately 7 when either acids or bases are added to them.
D) They maintain a relatively constant pH when either acids or bases are added to them.
E) They are found only in living systems and biological fluids.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Research indicates that acid precipitation can damage living organisms by
A) buffering aquatic systems such as lakes and streams.
B) decreasing the H⁺ concentration of lakes and streams.
C) increasing the OH⁻ concentration of lakes and streams.
D) washing away certain mineral ions that help buffer soil solution and are essential nutrients for plant growth.
E) both decreasing the H⁺ concentration of lakes and streams and increasing the OH⁻ concentration of lakes and streams.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many grams of acetic acid (C₂H₄O₂) would you use to make 10 L of a 0.1 M aqueous solution of acetic acid? (Note: The atomic masses, in daltons, are approximately 12 for carbon, 1 for hydrogen, and 16 for oxygen.)
A) 10 g
B) 0.1 g
C) 6.0 g
D) 60 g
E) 0.6 g
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider two solutions: solution X has a pH of 4; solution Y has a pH of 7. From this information, we can reasonably conclude that
A) solution Y has no free hydrogen ions (H⁺) .
B) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 30 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
C) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y is 1,000 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X.
D) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 3 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
E) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 1,000 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How would acidification of seawater affect marine organisms?
A) Acidification would increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
B) Acidification would decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
C) Acidification would increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.
D) Acidification would decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.
E) Acidification would increase dissolved bicarbonate concentrations, and cause increased calcification of corals and shellfish.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sulfur is in the same column of the periodic table as oxygen, but has electronegativity similar to carbon. Compared to water molecules, molecules of H₂S
A) will ionize more readily.
B) will have greater cohesion to other molecules of H₂S.
C) will have a greater tendency to form hydrogen bonds with each other.
D) will have a higher capacity to absorb heat for the same change in temperature.
E) will not form hydrogen bonds with each other.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have a freshly prepared 0.1 M solution of glucose in water. Each liter of this solution contains how many glucose molecules?
A) 6.02 × 10²³
B) 3.01 × 10²³
C) 6.02 × 10²⁴
D) 12.04 × 10²³
E) 6.02 × 10²²
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The slight negative charge at one end of one water molecule is attracted to the slight positive charge of another water molecule. What is this attraction called?
A) a covalent bond
B) a hydrogen bond
C) an ionic bond
D) a hydrophilic bond
E) a van der Waals interaction
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have two beakers. One contains pure water, the other contains pure methanol (wood alcohol) . The covalent bonds of methanol molecules are nonpolar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules. You pour crystals of table salt (NaCl) into each beaker. Predict what will happen.
A) Equal amounts of NaCl crystals will dissolve in both water and methanol.
B) NaCl crystals will NOT dissolve in either water or methanol.
C) NaCl crystals will dissolve readily in water but will not dissolve in methanol.
D) NaCl crystals will dissolve readily in methanol but will not dissolve in water.
E) When the first crystals of NaCl are added to water or to methanol, they will not dissolve; but as more crystals are added, the crystals will begin to dissolve faster and faster.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
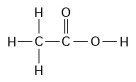 -How many grams of the compound in the figure above would be required to make 2.5 L of a 1 M solution?
(carbon = 12, oxygen = 16, hydrogen = 1)
-How many grams of the compound in the figure above would be required to make 2.5 L of a 1 M solution?
(carbon = 12, oxygen = 16, hydrogen = 1)
A) 29
B) 30
C) 60
D) 150
E) 342
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increased atmospheric CO₂ concentrations might have what effect on seawater?
A) Seawater will become more acidic, and bicarbonate concentrations will decrease.
B) Seawater will become more alkaline, and carbonate concentrations will decrease.
C) There will be no change in the pH of seawater, because carbonate will turn to bicarbonate.
D) Seawater will become more acidic, and carbonate concentrations will decrease.
E) Seawater will become more acidic, and carbonate concentrations will increase.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A slice of pizza has 500 kcal. If we could burn the pizza and use all the heat to warm a 50-L container of cold water, what would be the approximate increase in the temperature of the water? (Note: A liter of cold water weighs about 1 kg.)
A) 50°C
B) 5°C
C) 1°C
D) 100°C
E) 10°C
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize?
A) ionic bonds
B) both hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds
C) polar covalent bonds
D) hydrogen bonds
E) both polar covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One idea to mitigate the effects of burning fossil fuels on atmospheric CO₂ concentrations is to pipe liquid CO₂ into the ocean at depths of 2,500 feet or greater. At the high pressures at such depths, CO₂ is heavier than water. What potential effects might result from implementing such a scheme?
A) increased photosynthetic carbon fixation because of the increased dissolved carbon dioxide in the deep water
B) increased carbonate concentrations in the deep waters
C) reduced growth of corals from a change in the carbonate-bicarbonate equilibrium
D) no effect because carbon dioxide is not soluble in water
E) both increased acidity of the deep waters and changes in the growth of bottom-dwelling organisms with calcium carbonate shells
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -How many grams would be equal to 1 mol of the compound shown in the figure above?
(carbon = 12, oxygen = 16, hydrogen = 1)
-How many grams would be equal to 1 mol of the compound shown in the figure above?
(carbon = 12, oxygen = 16, hydrogen = 1)
A) 29
B) 30
C) 60
D) 150
E) 342
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the hydrogen ion [H⁺] concentration of a solution of pH 8?
A) 8 M
B) 8 x 10⁻⁶ M
C) 0.01 M
D) 10⁻⁸ M
E) 10⁻⁶ M
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 70
Related Exams